단절점
Updated:
단절점은 무향 연결 그래프에서 특정 정점을 제거 했을때 두개의 연결 그래프로 나뉘는 정점을 단절점이라고 한다
그림을 통해서 어떻게 가는지 한번 보자
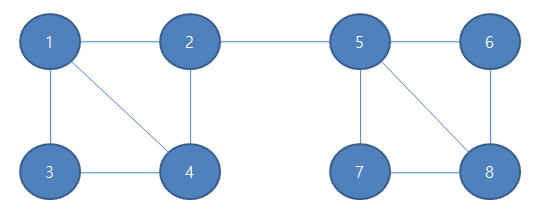
이런 무향그래프가 있다고 가정할때 아래와 같이 방문을 했다고 가정해보자
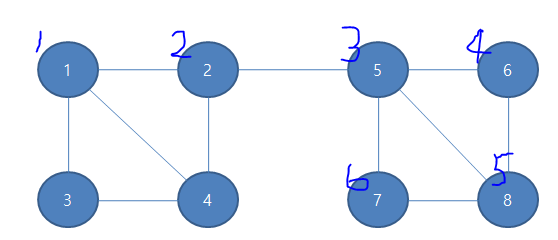
파란글씨는 방문순서
이제 6번째로 방문한 7번 노드는 주위에 더이상 갈곳이 없으니 5번으로 돌아올것이다
근데 이때, 돌아올때 우리는 리턴해주는 값을 설정할것이다
그 리턴해주는 값은 7번 노드와 연결된 가장 빨리 방문한 노드의 번호이다. 7번 노드에서 연결된 가장 빨리 방문한 노드는
5번 노드이기 때문에, 5번이 방문된 순서 3 값을 반환해줄 것이다.
그러면 이제 8번 노드로 다시 돌아오게 되는데, 여기서 단절점임을 확인해 줄수 있는것이,
현재정점(8번노드)보다 늦게 방문한(7번노드)정점의 리턴값이 내가 방문된 순서보다 같거나 크다면 이 정점은 단절점으로 체크를 한다는 것이다
그냥 간단하게 생각을 해보면, 단절점은 일종의 유일한 길목이라고 보면 된다. 즉, 현재정점보다 더 늦게 방문된 노드가 현재정점보다 더 일찍 방문된 노드로
갈수 있다면, 그건 애초에 현재정점이 유일한 길목이 아니게 되는것이다. 근데 만약 같다면,(사실 절대 작지도 않을것이다)
가장 빨리 갈수 있는 노드가 현재정점이기 때문에, 현재정점이 유일한 길목이 되게 되므로, 나를 단절점으로 보면될것이다
(여기서 나라는 의미는 정점으로 해석하시면 좋을것 같습니다)
그러므로 8번노드의 입장에서 본인의 방문순서인 5보다 3이 더 작기때문에, 단절점이 아니고, 8번노드또한 가장빨리 갈수 있는 노드 번호가
5번이므로 3을 반환해준다
이런식으로 진행을 하다보면
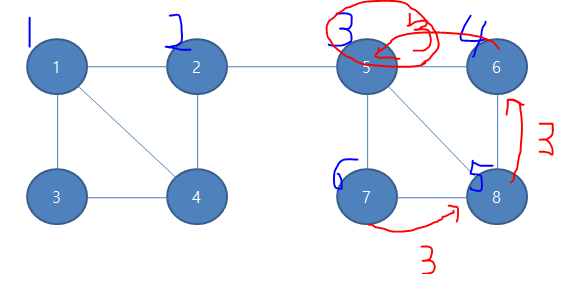
이렇게 5번정점을 단절점으로 체크하게 되는 경우가 생긴다. 그러면 단절점을 체크를 하고, 가장 빠른 방문순서 2(2번노드)를 반환해준다
그러면 2번 노드 또한 본인의 방문순서와 일치하므로 단절점을 체크해준다
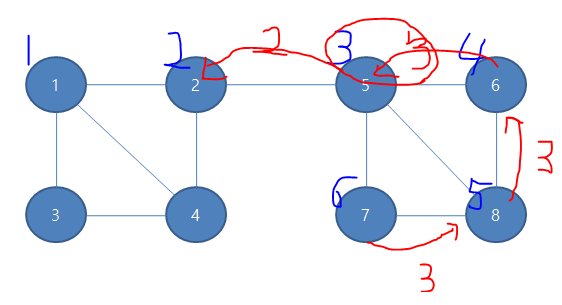
이런 식으로 계속 진행하면 결국 끝에는 이런 그림이 나오게 된다
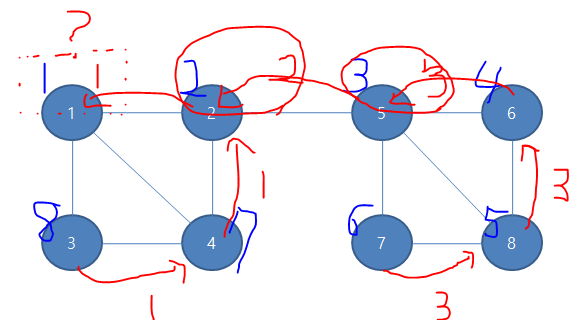
근데 단절점의 특징중 하나가 있는데, 루트에서 시작(여기서는 1번정점)한 경우는 위와 같은 방식으로 단절점을 체크하지는 않습니다
루트가 단절점이 되려면, 루트에서 방문한 노드의 갯수가 2개 이상이어야 루트가 단절점이 될수 있습니다
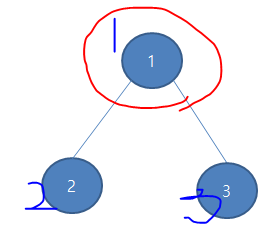
그러므로, 1번 정점에서 호출한 자식은 2번 정점밖에 없기 때문에, 갯수는 1개가 되고, 단절점으로 판단하지 않는다는 것입니다
관련 문제는 다음과 같습니다. https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11266
by C++
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <set>
#include <list>
#include <climits>
#include <string.h>
#include <deque>
#include <functional>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define INF 1000000000
typedef pair<int, ll> P;
typedef pair<pair<int, int>, int> PP;
typedef pair<int, pair<int, int>> PPP;
int gox[4] = { 0,1,-1,0 };
int goy[4] = { 1,0,0,-1 };
vector<vector<int>> a;
int dis[10005];
int cutvertex[10005];
int n, m, t;
int dfs(int here, bool ok) {
dis[here] = ++t;
int ret = dis[here];
int child = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a[here].size(); i++) {
int next = a[here][i];
if (!dis[next]) {
child++; //루트에서 호출된 자식을 카운트
int r = dfs(next, false); //자식들중에서 가장 먼저 방문된번호
if (!ok && r >= dis[here]) {
cutvertex[here] = true;
}
ret = min(ret, r); // 항상 최솟값 갱신
}
else ret = min(ret, dis[next]); // 인접한 노드 중에 최솟값 갱신
}
if (ok && child >= 2) cutvertex[here] = true; // 루트도 단절점이다
return ret;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
a.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int first, second;
scanf("%d%d", &first, &second);
a[first].push_back(second);
a[second].push_back(first);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!dis[i]) { // 여러개의 그래프가 입력될수 있기 때문에, n번씩 돌면서 다해줘야함
dfs(i, true);
}
}
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (cutvertex[i]) v.push_back(i);
}
printf("%d\n", v.size());
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
printf("%d ", v[i]);
}
return 0;
}
by Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import static java.lang.Integer.min;
public class Main {
static BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static int t = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
List<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
int[] dis = new int[n + 1];
boolean[] cut = new boolean[n + 1];
ArrayList<Integer> v = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int here = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()), next = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
graph[here].add(next);
graph[next].add(here);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (dis[i] == 0) dfs(i, true, cut, dis, graph);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (cut[i]) v.add(i);
}
bw.write(v.size() + "\n");
for (Integer e : v) {
bw.write(e + " ");
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
private static int dfs(int here, boolean ok, boolean[] cut, int[] dis, List<Integer>[] graph) {
dis[here] = ++t;
int child = 0;
int ret = dis[here];
for (int i = 0; i < graph[here].size(); i++) {
int next = graph[here].get(i);
if (dis[next] == 0) {
child++;
int r = dfs(next, false, cut, dis, graph);
if (!ok && r >= dis[here]) {
cut[here] = true;
}
ret = min(ret, r);
} else ret = min(ret, dis[next]);
}
if (ok && child >= 2) cut[here] = true;
return ret;
}
}

Leave a comment